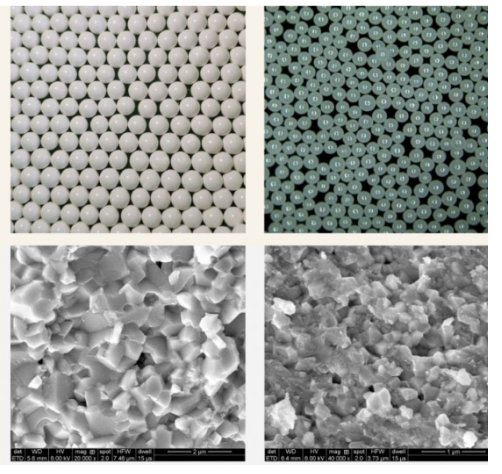
High-End Ceramic Precision Balls
The ceramic balls used in the market mainly include silicon nitride ceramic ball, zirconium oxide ceramic ball, silicon carbide ceramic ball, high purity alumina ceramic ball. Silicon nitride has become the most widely used variety because of its superior comprehensive performance. The reason why precision ceramic balls can replace steel balls is their low density, medium elastic modulus, low thermal expansion coefficient and excellent intrinsic chemical characteristics. The following table makes a brief comparison of the main properties of the four materials.

Table 1 Comparison of properties of common materials and characteristics
| material | density | hardness | coefficient of expansion due to heat | modulus of elasticity | fracture toughness |
| silicon nitride | 3.2 | 1500 | 3.2 | 310 | 7.0-8.0 |
| zirconia | 6.2 | 1250 | 10.5 | 210 | 10.0 |
| carborundum | 3.1 | 2500 | 4.5 | 350 | – |
| alumina | 3.7 | 1800 | 8.5 | 380 | 3.0-4.0 |
Ceramic precision balls Application
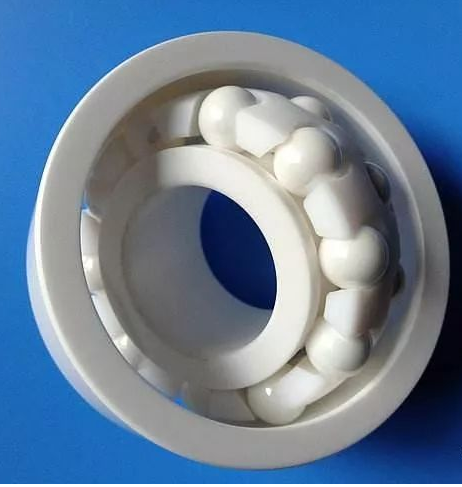
For the core component of ceramic ball bearing —— ceramic ball, precision ceramic ball has small density, high hardness, high elastic modulus, wear resistance, low thermal expansion coefficient, good thermal stability and chemical stability, insulation, no magnetic and other excellent comprehensive performance. Among them, silicon nitride is considered to be the best material for making bearing rolling body, and has achieved great success in ceramic ball bearing applications. Ceramic ball bearings can operate without adding any oil, avoiding the occurrence of premature bearing damage caused by oil drying in ordinary bearings. At present, ceramic ball has been widely used in aerospace, military, petroleum, chemical industry and high-speed precision machinery and many other fields.

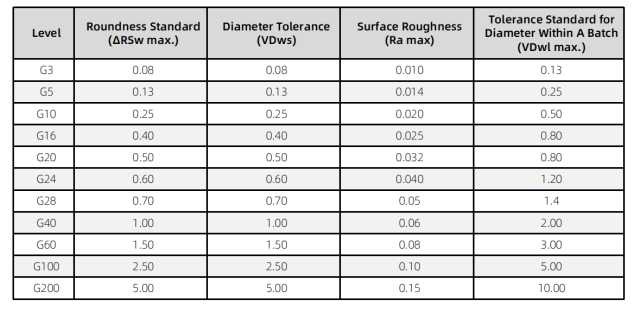
Table 3 Important indicators of precision grade
| grade | The precision of the ball is represented by the number, and the smaller the number is |
| out of roundness | The radius direction distance of the surface and the small sphere and the radius direction distance of the surface of the sphere are used for the true roundness of the sphere |
| surface roughness | Different series spheres have different surface coarse ranges |
| Batch diameter tolerance | The difference between the mean diameter and the large ball in the same production batch |
Ceramic precision ball Accuracy Grade Table (Unit:um)

Any question or demand of the ceramic precision ball, welcome to contact us at sales@inlabs.cc.