What is alumina crucible?
Crucibles are built of high-temperature resistant materials and used in chemistry labs as containers for extremely hot chemical substances. In addition, alumina is frequently utilized in ceramic form due to its strength, inexpensive cost, and capacity to tolerate temperatures of up to 1,600℃ (approx. 2,912℉)..Alumina is the most widely used Fine Ceramic today globally and epitomizes Fine Ceramics. It offers superior mechanical strength, electrical insulation, high frequency retention, thermal conductivity, heat resistance and corrosion resistance. Sapphire is a single-crystal form of alumina.
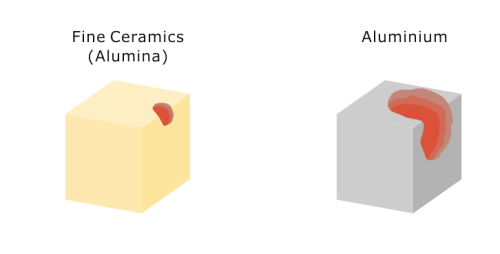
While aluminum begins to melt at approximately 660℃ (approx. 1,220℉), alumina Fine Ceramics only begin to melt or decompose at temperatures above 1,600℃ (approx. 2,912℉).

When materials are heated, their size and volume increase in small increments, in a phenomenon known as thermal expansion. Expansion values vary depending on the material being heated. The coefficient ratio of thermal expansion indicates how much a material expands per 1℃ (2.2℉) rise in temperature. Alumina fine ceramics have low coefficients of thermal expansion — less than half those of stainless steels.
It is resistant to chemical attacks from most acids and alkaline solutions as well as hydrogen and other reducing gases, with the exception of :
High concentration hydrofluoric acid
Phosphoric acid at boiling point
Potassium hydroxide solution at boiling point
Sodium hydroxide solution
Alkali salt melt
Composition:
Al2O3 Alumina 99.7% with traces of MgO Magnesia and SiO2 Silica.
Maximum usage temperature: 1700°C
Good resistance to thermal shock
High electrical resistivity
Good mechanical resistance
Available products:
Cylindrical crucibles
Conical crucibles
Tubular crucibles
Incineration tanks
Dishes
